UGC NET Subject wise MCQs (Paper 1 & 2)
UGC NET (Paper 1) Mock Tests
UGC NET (Paper 2) Mock Tests
LawVidhi Super 30 – UGC NET (LAW) JRF Target Batch
UGC NET (Law) Eligibility Criteria
Educational Qualification: The primary criterion is a Master’s degree in Law from a recognized university, with a minimum of 55% marks (50% for reserved categories). Candidates who are pursuing their Master’s or have appeared for their final year exams are also eligible, subject to passing with the required percentage.
Age Limit: For JRF (Junior Research Fellowship), the upper age limit is 31 years, with age relaxation applicable for reserved categories. For Assistant Professorship, there is no upper age limit.
UGC NET PAPER 1 – SUBJECT-WISE BIFURCATION
| Sr. No. | Unit Name | No. of Questions (Approx.) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Teaching Aptitude | 5–6 |
| 2 | Research Aptitude | 5–6 |
| 3 | Comprehension | 5 |
| 4 | Communication | 4–5 |
| 5 | Mathematical Reasoning and Aptitude | 5–6 |
| 6 | Logical Reasoning | 5–6 |
| 7 | Data Interpretation (DI Table or Graph) | 5 |
| 8 | Information and Communication Technology (ICT) | 4–5 |
| 9 | People, Development and Environment (PDE) | 5–6 |
| 10 | Higher Education System: Governance, Polity & Admin | 5–6 |
UGC NET LAW Paper 2 – SUBJECT-WISE QUESTION BIFURCATION
| Sr. No. | Subject Area | No. of Questions (Approx.) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Jurisprudence | 8–10 |
| 2 | Constitutional Law | 10–12 |
| 3 | Administrative Law | 4–6 |
| 4 | Public International Law | 5–7 |
| 5 | Law of Crimes (IPC, CrPC, Evidence) | 8–10 |
| 6 | Law of Torts incl. Consumer Protection | 4–6 |
| 7 | Family Law (Hindu + Muslim) | 5–6 |
| 8 | Law of Contracts (General + Special) | 5–7 |
| 9 | Company Law & Partnership | 4–5 |
| 10 | Environmental Law | 3–5 |
| 11 | Human Rights & Humanitarian Law | 3–5 |
| 12 | IPR (Intellectual Property Rights) | 2–4 |
| 13 | International Economic Law (WTO etc.) | 1–2 |
| 14 | Cyber Law / Contemporary Legal Developments | 2–3 |
| 15 | Legal Research & Methodology | 4–6 |
Exam Pattern: A Closer Look
The UGC NET (Law) consists of two papers, conducted in a single three-hour session.
- Paper 1: This is a general paper common to all subjects, testing teaching/research aptitude. It comprises 50 objective-type questions, each carrying 2 marks.
- Paper 2: Specific to Law, this paper includes 100 objective-type questions, each carrying 2 marks, designed to assess the candidate’s subject knowledge and application skills.
UGC NET (LAW) Exam Analysis
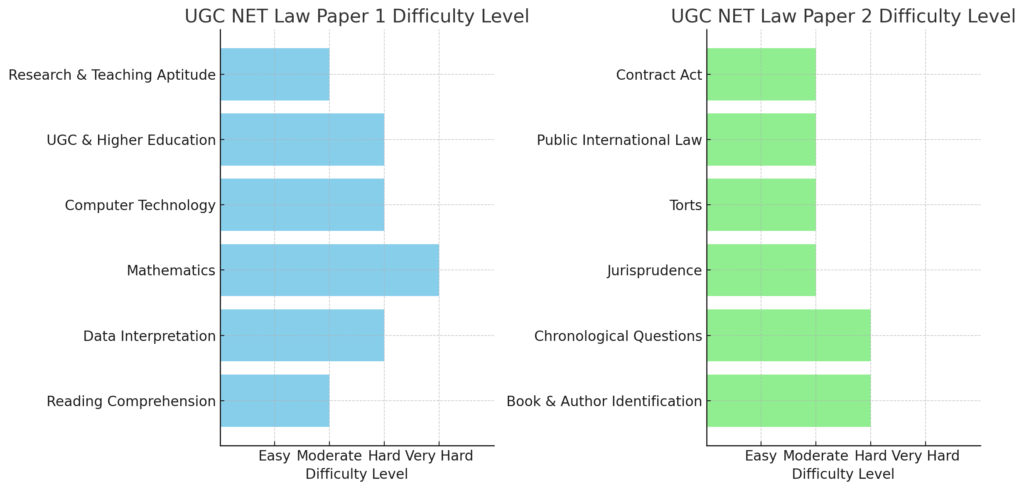
Paper 1 Analysis:
- Reading Comprehension: Moderately challenging, requiring decent preparation.
- Data Interpretation: Slightly more difficult, demanding a good grasp of the subject.
- Mathematics: Found to be quite hard, especially for those weak in this area.
- Computer Technology: Also of moderate difficulty, reflecting the recent emphasis on tech-savvy questions.
- UGC & Higher Education: Moderate level, reflecting a fair number of questions in this area.
- Research & Teaching Aptitude: Easier than last year, making it approachable for well-prepared candidates.
Paper 2 Analysis:
- Book & Author Identification: More challenging, demanding specific knowledge.
- Chronological Questions: Equally challenging, requiring a detailed understanding of timelines.
- Jurisprudence, Torts, Public International Law, and Contract Act: These sections were relatively easier compared to others, but still required a solid understanding of the law.
Syllabus: What to Expect?
Paper 1: The syllabus includes teaching aptitude, research aptitude, reading comprehension, communication, reasoning (including mathematical), logical reasoning, data interpretation, information and communication technology (ICT), people and environment, and higher education system.
Paper 2 (Law): It covers a wide array of topics such as Constitutional Law, Legal Theory, Public International Law, Family Law, Law of Torts, Law of Crimes, Labour Law, Environmental Law, Human Rights, and practices, and much more.
Conclusion
The UGC NET (Law) exam is a gateway to a fulfilling career in legal education and research. With the right preparation and understanding of the eligibility criteria, exam pattern, and syllabus, you can pave your way towards achieving your academic aspirations. Remember, consistency and persistence are key. Good luck!
































